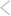Orphan drugs are specialized medications developed for treating rare diseases that have an effect on a small percentage of our population. These diseases, often overlooked by traditional drug development due to limited market potential, are now gaining attention thanks to incentives and support from global health authorities. Orphan drugs play a crucial role in addressing unmet medical needs and advancing treatments for conditions that were previously neglected.
Unmet Medical Needs
Despite progress, 95% of rare diseases – among the 7,000 to 10,000 identified globally – lack Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved treatments. In the U.S., over 25 million people are affected by rare diseases, yet only a small percentage have access to approved therapies. Of the few available treatments, two-thirds of rare diseases have only one or two approved products, highlighting the substantial unmet medical need. While orphan drug designation provides regulatory incentives such as market exclusivity and reduced fees, the vast number of untreated diseases presents significant opportunities for pharmaceutical innovation, potentially transforming the lives of millions with limited or no treatment options.
Today, only 5% of rare diseases have an FDA-approved therapy.
Orphan Drug Designation
Orphan drug designation is a unique status granted by regulatory agencies like the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to encourage the development of treatments for rare diseases. The FDA describes a rare disease as one that affects fewer than seven in 200,000 people, while the EMA considers a disease rare if it affects less than five in 10,000 people, highlighting variations in global definitions.
Criteria to define rare disease: <7 in 200,000 people in the U.S. and <5 in 10,000 people in the EU.
Growing Importance of Orphan Drugs Development in Rare Disease Treatment and Drug Development
Orphan drugs target rare diseases that affect a small segment of the population, impacting approximately 350 million people globally, including 25–30 million in the U.S. Despite their rarity, orphan drugs have become a vital focus of pharmaceutical innovation. In the past five years, orphan medicines have accounted for more than half of all new drug approvals in the U.S. and around 45% in Europe. For instance, 53% of the 268 drug launches in the U.S. during this period were designated as orphan drugs, reflecting a growing emphasis on rare diseases. Moreover, approximately 44% of global clinical trials are aimed at rare diseases, underscoring the importance of orphan drugs in current medical advancements.
Market Overview of Orphan Drug Development
The global orphan drugs market has experienced impressive growth, valued at $170.49 billion in 2023. Projections indicate that the market will continue its upward trajectory, expected to grow from $189.17 billion in 2024 to an astonishing $468.58 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 12.0% during this period. North America dominated the global market with a commanding 53.94% share in 2023.
Market Trends of Orphan Drug Development
According to the 2022 Orphan Drug Report by Evaluate Pharma, the top 10 orphan drug blockbusters are anticipated to be valued between $3.0 billion and $13 billion by 2026. Notably, 40% of Johnson & Johnson’s pharmaceutical revenue is expected to be derived from orphan drugs, with key contributors like the blood cancer treatments Imbruvica and Darzalex projected to exceed $23.0 billion by 2026. The launch of these advanced therapeutics by both established and emerging companies is driving increased adoption and contributing to significant market growth.
Read more: Healthcare Market Research in the Era of New Technology
Market Segmentation of Orphan Drug Development
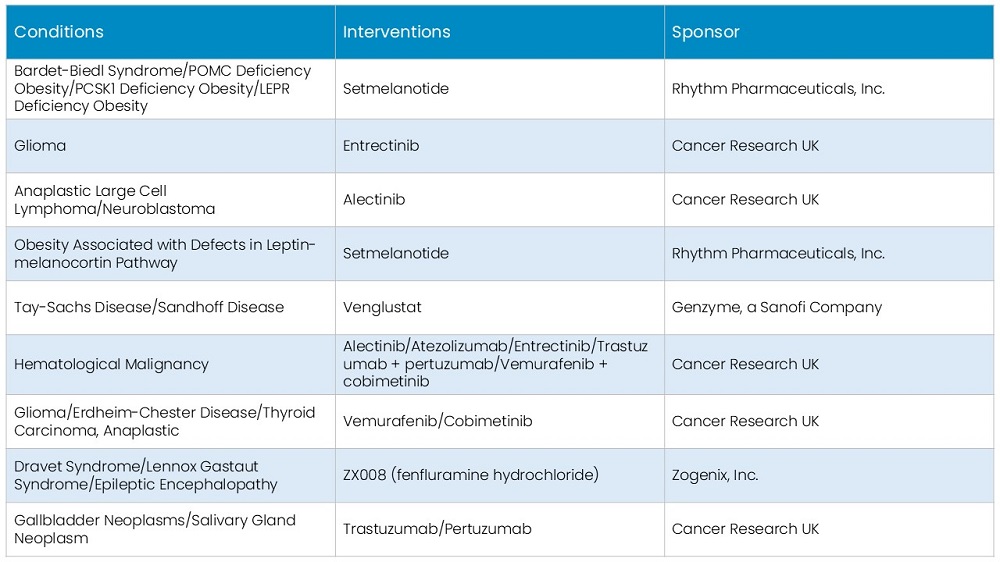
In 2023, the oncology segment emerged as the dominant player in the orphan drugs market. This can be attributed to the strong pipeline of oncology drugs being developed by major companies and the prevalence of orphan drugs dedicated to cancer treatment. For example, in February 2022, CTI BioPharma received FDA approval for Pacritinib, a treatment for myelofibrosis - a rare bone cancer - that affects over 21,000 patients in the US.
The hematology segment is considered to be the second most dominant, driven by a surge in new product launches and a number of regulatory approvals. The introduction of novel therapeutics for blood-related disorders is expected to bolster the segment’s growth.
Figure: Global Orphan Drug Market Share By Therapy Area, 2023
Regional Insights
North America held a dominant position in the global orphan drugs market, valued at $91.97 billion in 2023, accounting for nearly 54% of global sales. This is primarily due to significant investments in orphan drugs, a strong patient base, and the presence of key market players driving the development of cutting-edge treatments.
Key Market Players and Competitive Landscape
The global orphan drug market is extremely competitive, driven by both established and emerging pharmaceutical companies with diverse and innovative product development pipelines. In 2023, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. dominated the market, largely due to their strong portfolios in oncology-related drugs. Their leadership is a testament to the increasing demand for orphan drugs that address rare diseases, particularly in the oncology segment.
However, the landscape is rapidly evolving, with companies such as Biogen Inc. and BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. emerging as key players with innovative solutions targeting various rare diseases. These companies are focusing on expanding their orphan drug portfolios, which is aiding in their growth and market penetration.
Other prominent players, including Amgen Inc. (U.S.), Bayer AG (Germany), Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc. (U.S.), Novo Nordisk A/S (Denmark), Novartis AG (Switzerland), AstraZeneca (U.K.), Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited (Japan), and GlaxoSmithKline plc (U.K.), are also making significant contributions to market growth. With their global presence and commitment to addressing unmet medical needs through novel orphan drugs, these companies are driving advancements in rare disease treatments and positioning themselves at the forefront of the market.
List of FDA-approved Orphan Drugs Developed by Leading Companies (2024)
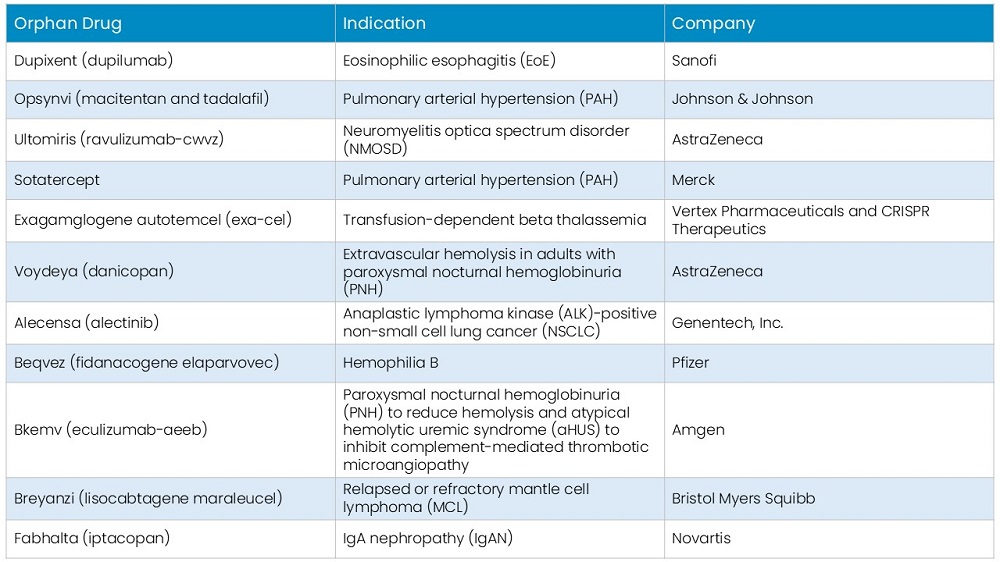
Overview of Active Phase 2/3 Clinical Trials for Rare Disease Treatments
Orphan Drug Act (1983)
The Orphan Drug Act (ODA) of 1983 is U.S. legislation aimed at promoting the development of drugs for rare diseases affecting fewer than 200,000 individuals in the country. The Act offers incentives such as 7 years of market exclusivity and tax credits for clinical research, along with grants to support development. It also provides regulatory assistance and fee waivers to reduce financial burdens. Since its enactment, the ODA has significantly increased the availability of orphan drugs, improving treatment options for rare disease patients and influencing similar policies internationally.
Government Incentives for Orphan Drug Development
Governments worldwide have introduced both financial and non-financial incentives to stimulate rare disease drug development, addressing the unmet needs associated with rare diseases.
Financial Incentives
- Tax Credits and R&D Grants: Significant financial support includes tax credits and grants that help offset drug development costs, with specialized grants for pediatric rare disease drug development due to the high incidence of rare diseases in children.
- Regulatory Fee Waivers: Many governments offer reduced or waived fees for regulatory processes, including drug application filings.
Non-financial Incentives
- Accelerated Review Timelines: Agencies like the FDA and EMA expedite clinical and regulatory review times. For example, U.S. clinical reviews have been reduced by about 18 months, and regulatory reviews have been reduced by eight months.
- Reduced Clinical Trial Sizes: Orphan drug trials often require fewer participants, with Phase III trials needing a median of 538 participants compared to 1,491 for non-orphan drugs, easing logistical and financial burdens.
- Extended Market Exclusivity: Orphan drugs receive extended market exclusivity – seven years in the U.S. and up to 10 years in the EU – allowing companies to recoup costs by delaying competition.
- Improved Market Access: Governments enhance market access through subsidies, outcome-based payment models, and pricing programs to make orphan drugs more affordable.
- Technology Adoption: Incentives also encourage investment in advanced therapies, such as gene and cell therapies, which offer potential curative treatments for rare diseases.
These incentives collectively boost R&D investment in orphan drugs, particularly in oncology, neurology, and hematology, while supporting the development of advanced therapies.
Read more: Importance of Data Analytics in the Healthcare Industry
Challenges in Orphan Drug Development
Orphan drug development faces numerous challenges due to the unique complexities of rare diseases, as well as associated regulatory, logistical, and financial issues.
- Limited Knowledge and Complex Disease Mechanisms: Rare diseases often have complex, poorly understood mechanisms and various subtypes, making it challenging to develop effective treatments. The lack of preclinical models and biomarkers further complicates clinical trial design and efficacy assessment.
- Small Patient Populations: Recruiting patients for trials is challenging due to small and geographically dispersed populations, leading to logistical issues and higher risks of zero-enrollment sites.
- High R&D Costs: The cost of developing orphan drugs is amplified by the smaller patient base and longer trial timelines. With a limited market size, the return on investment is low, making it financially challenging for companies to pursue these treatments.
- As reported by USA Today in 2023, Zolgensma, a one-time treatment approved for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), is among the highest-priced drugs in the U.S. market. The drugs cost around $2.25 million and have treated more than 3,000 patients globally.
- Clinical Trial Design Complexities: Designing trials for rare diseases requires innovative approaches to maximize the limited patient pool while adhering to complex regulatory requirements.
- Regulatory and Pricing Challenges: Regulatory authorities now demand more evidence of therapeutic value and comparative effectiveness, which can lengthen trial timelines. Additionally, increased scrutiny of drug prices forces companies to negotiate with payers and offer significant discounts.
- Awareness and Patient Identification: Low awareness among healthcare professionals (HCPs) and the public complicates diagnosis and patient recruitment. Personalized approaches and partnerships with patient advocacy groups (PAGs) are crucial for addressing these gaps.
- Patient Journey and Referral Patterns: Complex diagnostic and treatment pathways make accurate and timely diagnosis challenging. Understanding patient journeys and referral patterns is essential for effective collaboration with healthcare providers.
Opportunities in Orphan Drug Development: Overcoming Challenges and Unlocking Potential
Orphan drug development, despite its challenges, offers significant opportunities for life sciences companies to make a positive impact on patients’ lives. By adopting patient-centric approaches and leveraging advanced digital and analytical capabilities, companies can address these challenges and bring transformative therapies to market.
-
Leveraging Digital and Analytical Innovations
Digital technologies and advanced analytics offer new opportunities in orphan drug development. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can help improve patient identification and diagnostic processes, while digital health platforms support patient management and adherence with the help of symptom checkers and remote monitoring tools.
-
Enhancing Patient Recruitment and Retention
To overcome recruitment and retention challenges, companies should develop robust strategies and engage with PAGs. Effective support and solutions can be developed by understanding patient needs and providing comprehensive trial support.
-
Expanding Patient Access and Support
Early-access programs and expanded support services are crucial for reaching patients. Partnerships with third-party institutions, specialist nursing services, help lines, and educational resources can enhance access and improve treatment outcomes.
-
Collaborating with PAGs
PAGs are essential in raising awareness, advocating for funding, and managing patient registries. Collaboration with PAGs helps amplify patient voices, bridge data gaps, and translate complex information into accessible language, which can improve reimbursement strategies.
-
Navigating Reimbursement and Policy Challenges
The reimbursement landscape for orphan drugs is complex. Companies must engage with payers and regulatory agencies to navigate fragmented systems and evolving policies, ensuring fair reimbursement and accessibility of new therapies.
-
Driving Innovation Through Real-world Evidence
Real-world Evidence (RWE) is increasingly valuable in orphan drug development, providing insights into disease presentation and treatment effectiveness. Incorporating RWE supports clinical and regulatory decisions, informs development strategies, and addresses traditional trial design limitations.
Future & Emerging Trends
Tech Advancements in Orphan Drug Development
The landscape of orphan drug development is evolving rapidly due to advancements in technology, offering new opportunities for tackling rare diseases. These advancements – spanning precision medicine, gene and cell therapies, and AI-powered digital health tools – are not only transforming the way treatments are developed but also enhancing patient support, diagnosis, and engagement.
-
Precision Medicine and Genomics
Precision medicine is transforming rare disease treatment by utilizing genomic data to develop highly targeted therapies tailored to individual patients’ genetic profiles. This approach assists with the identification of specific genetic mutations responsible for rare diseases, leading to more effective and personalized treatments.
Advances in genomics have facilitated the development of therapies that directly address these mutations, minimizing the trial-and-error approach common in traditional treatments. For example, therapies for cystic fibrosis are now designed to target specific genetic abnormalities, significantly improving patient outcomes and reducing treatment-related side effects.
Read more: Prognosis 2024: Unveiling Healthcare Trends and Strategies
-
Gene and Cell Therapies
Gene and cell therapies represent groundbreaking advancements in treating rare diseases by addressing their genetic causes. Gene therapy involves introducing, removing, or altering genetic material within a patient’s cells to correct genetic defects. This method holds promise for conditions caused by single-gene mutations, such as hemophilia, potentially offering lifelong benefits with a single treatment.
Cell therapy, on the other hand, involves replacing damaged cells or tissues with healthy ones. This approach is particularly successful in treating rare blood disorders and certain cancers. A notable success story is Zolgensma, a gene therapy for SMA, which has shown remarkable results in halting disease progression and improving motor function with just one administration.
-
Digital Health and AI
Digital health technologies and AI are enhancing the management and development of treatments for rare diseases. AI is revolutionizing diagnostics by analyzing extensive datasets, including genetic, clinical, and imaging information, to identify patterns and expedite accurate diagnoses.
Digital health tools, such as patient apps and wearables, enable continuous symptom tracking, providing real-time insights into disease progression and treatment efficacy. Telemedicine platforms facilitate remote consultations with specialists, reducing the need for patients to travel for expert care.
AI-powered diagnostics can uncover subtle patterns in patient data that may not be evident to clinicians, leading to earlier and more precise diagnoses. Additionally, remote patient monitoring technologies help track vital signs and detect early signs of complications, improving patient management and outcomes.
Patient-centric Approaches in Rare Disease Treatment: Leveraging RWE
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the need for patient-centric strategies in rare disease treatment. Advances in digital technology and analytics are reshaping how therapies are developed and refined, with RWE playing a central role.
-
Embracing a Patient-centric Approach
Understanding the Rare Disease Community: Rare disease communities are tight-knit, with significant interactions between patients, caregivers, and PAGs. A patient-centric approach requires a deep understanding of the patient’s journey, from diagnosis to treatment, along with ongoing innovation to address unmet needs.
Engagement with HCPs: Collaboration with HCPs is crucial for gaining insights into disease characteristics and ensuring that treatments meet patient needs. Close partnerships help align development efforts with real-world requirements and improve treatment outcomes.
-
Leveraging Data and AI for Patient Identification and Disease Diagnosis
Advanced Analytics and ML: Identifying and understanding rare disease populations is challenging due to their small and dispersed nature. Advanced analytics and ML can map patient groups and highlight unmet needs, enabling targeted engagement and education.
Accelerating Diagnosis: Diagnosing rare diseases can be a lengthy process, often leading to worsened symptoms. Data-driven approaches, and large datasets now allow for faster identification and intervention, potentially improving disease outcomes through earlier treatment.
-
Innovating and Expanding Patient Access
Early-access Programs: Early-access programs enhance distribution and address funding gaps by providing early treatment opportunities and building partnerships with third-party institutions. These programs ensure that new therapies reach patients more quickly.
Utilizing RWE: RWE offers valuable insights into disease presentation and treatment efficacy in real-world settings. It can complement or even substitute traditional clinical trial data, refine trial designs, assess health threats, and inform regulatory decisions.
Examples of RWE Utilization: Between January 2019 and June 2021, 116 of 378 FDA approvals incorporated RWE. The FDA’s 2023 guidance underscores the importance of early engagement in planning RWE usage to effectively address rare disease challenges and improve patient outcomes.
Expanding Patient and Caregiver Support With Digital Technologies
- Digital Health Platforms: Digital tools like AI-enabled symptom checkers, remote monitoring, and adherence apps are revolutionizing patient support. These technologies improve symptom management, enhance treatment adherence, and offer real-time education.
- Education and Support Services: After diagnosis, patients and caregivers need substantial support. Digital health platforms and specialist services, including nursing support and helplines, are vital for providing ongoing education and guidance throughout the treatment journey.
- Online Presence and Advocacy: Strengthening online presence through digital marketing and advocacy raises awareness about rare diseases and available treatments. Engaging with PAGs and using digital strategies can help address awareness gaps and improve outreach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of orphan drug development looks promising, but demands continued dedication and innovation. The synergy between advanced technologies, patient-focused strategies, and supportive policies creates a powerful framework for addressing the unmet demands of patients with rare diseases.
However, overcoming the inherent challenges requires not only technological breakthroughs but also collaborative efforts across the industry, regulators, and patient communities. By staying adaptable and committed to these goals, we can make significant strides toward delivering effective treatments as well as enhancing the quality of life for patients with rare conditions.
About SG Analytics
SG Analytics (SGA) is an industry-leading global data solutions firm providing data-centric research and contextual analytics services to its clients, including Fortune 500 companies across BFSI, Technology, Media & Entertainment, and Healthcare sectors. Established in 2007, SG Analytics is a Great Place to Work® (GPTW) certified company with a team of over 1200 employees and a presence across the U.S.A., the UK, Switzerland, Poland, and India.
A leader in the healthcare domain, SG Analytics assists healthcare companies in leveraging the power of information. Contact us today if you are in search of efficient Healthcare solutions to make sound business decisions.
Apart from being recognized by reputed firms such as Gartner, Everest Group, and ISG, SGA has been featured in the elite Deloitte Technology Fast 50 India 2023 and APAC 2024 High Growth Companies by the Financial Times & Statista.