Apple continues to build on its fintech aspirations. The US technology giant recently launched a savings account linked with its Apple Card, which will offer a high annual percentage yield of 4.15%. The offering, in collaboration with Goldman Sachs, will need no fee, no minimum deposits, and no minimum balance requirements. The move is part of the ongoing trend of big tech’s entry into the banking and fintech space, offering innovative and disruptive financial products and services. While traditional banks have long dominated the financial services industry, moves like these are beginning to change the status quo and the shift is likely to have significant implications for both the financial services industry and consumers alike.
Apple is Not Alone
While tech giants have been experimenting with financial services for more than a decade, the speed at which they are expanding into this space has significantly accelerated in recent years. The dominance of fintech is inevitable, given that practically everyone has access to online banking or a smartphone app that is linked to their bank account. This increased pace can be attributed to several factors, including advancements in digital technology, changing customer expectations, and the growing importance of data in financial services. With the rise of digital banking and the increasing adoption of mobile devices, tech giants have recognized the potential for disruption in the financial services industry and are moving quickly to capitalize on this opportunity.
Read more: Deploying Technology to Cultivate a Digital Transformation Strategy that Delivers
Despite the proliferation of financial technology start-ups in recent years, traditional banks have never been too concerned about competition from these upstarts. Instead, banks have tended to view fintech companies as potential partners in innovation, leading to a symbiotic relationship that combines the strengths of both parties. However, the rise of big tech companies like Amazon, Apple, and Google has caused banks to sit up and take notice. With their vast distribution networks, low cost of capital, and unparalleled access to consumer and business data, these companies represent a serious threat to the traditional banking industry. For instance, there is a significant opportunity for big tech companies in digital payments, which is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.7% between 2023 and 2027, with total transaction value reaching $3.5 trillion by the end of the period, according to Statista. This represents a massive opportunity for big tech companies to disrupt the payments landscape and potentially displace traditional banks.
Fig 1: Factors Driving Big Tech Activity in Financial Sector

Source: CB Insights
Read more: Investment Trends 2023: Top Tech Stocks to Keep an Eye On
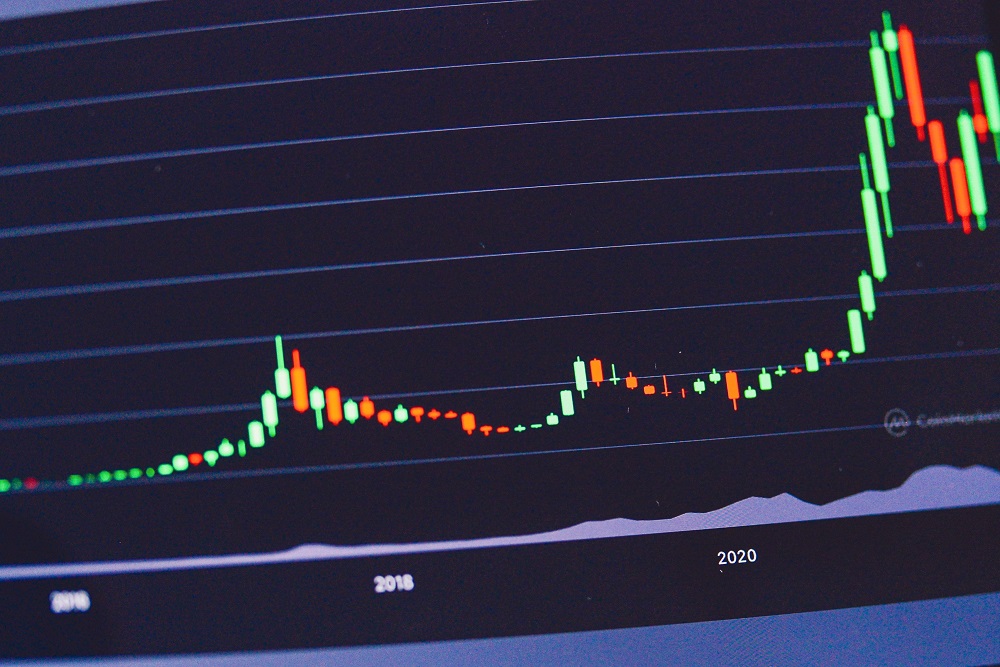
Apple’s fintech strategy has revolved around leveraging its ecosystem of devices and services to offer a seamless, secure, and personalized experience for its customers. One of the key elements of this strategy has been the launch of the Apple Card, a credit card that integrates with Apple Pay and offers cashback rewards. Apple’s partnership with Goldman Sachs goes back to when it partnered with the latter to offer personal loans to Apple Card customers and has introduced features to help users manage their finances, such as spending tracking and budgeting tools. Apple's ecosystem of devices, services, and partnerships gives it a strong foundation to build out its fintech offerings, and the company's focus on privacy and security is a key differentiator in the crowded fintech space.
Fig 2: Apple’s FinTech Playbook
Source: Whitesight
In addition to Apple, Amazon has been steadily expanding its presence in the fintech space over the last few years, building a comprehensive ecosystem of financial products and services for its customers. The company has partnered with banks to offer checking accounts, introduced Amazon Cash for customers to add cash to their Amazon balance, and launched its own digital wallet, Amazon Pay. In addition, Amazon has introduced credit products, such as the Amazon Store Card and Amazon Prime Rewards Visa Card.
Fig 3: Amazon’s Fintech Ecosystem

Source: CB Insights
Read more: A Way Forward: Cybersecurity Trends to Watch out for in 2023
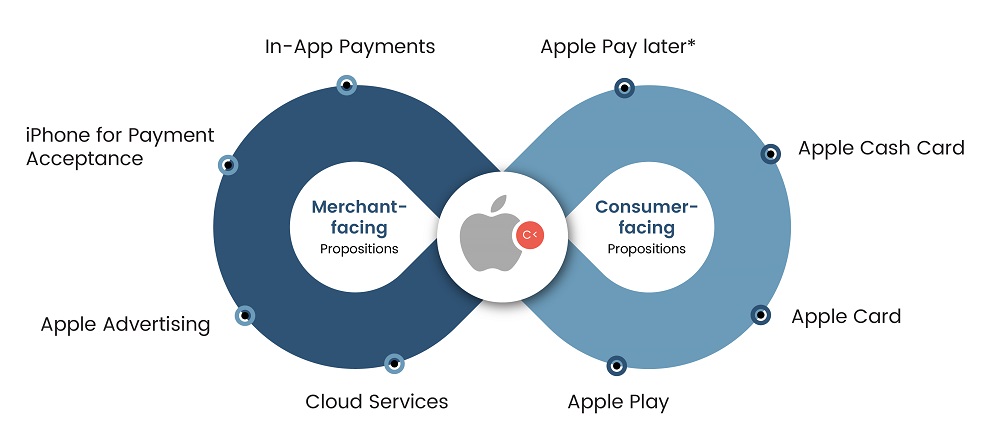
In the same vein, companies like Meta, Google, Uber, and Walmart have also dabbled with financial services. Meta is focused on payments, e-commerce, and NFTs, and aims to be the go-to wallet for Metaverse. Meta’s WhatsApp also rolled out P2P payments for user contacts in India and Brazil. Google’s Gradient Ventures is the most active big tech venture arm in fintech and invested in 32 deals between 2018 and 2022. Google also has a strong focus on digital enablement for banks, payments, and e-commerce. The company also expanded its partnership with Shopify to include YouTube and SMBs.
Fig 4: Companies are Making Fintech Move
Source: SG Analytics
Smaller Banking Players are at More Risk
The banking crisis stemming from Silicon Valley Bank’s collapse has raised concerns among smaller and regional banks. Owing to the collapse, consumers are shifting billions of dollars from smaller lenders to the “too-big-to-fail” banks. For instance, according to Bloomberg, Bank of America had received more than $15 billion in deposits post-SVB collapse. Moreover, large banks are reporting massive profit growths in Q1 2023, rebuilding the trust of consumers.
Fig 5: First Quarter Results of Major Banks
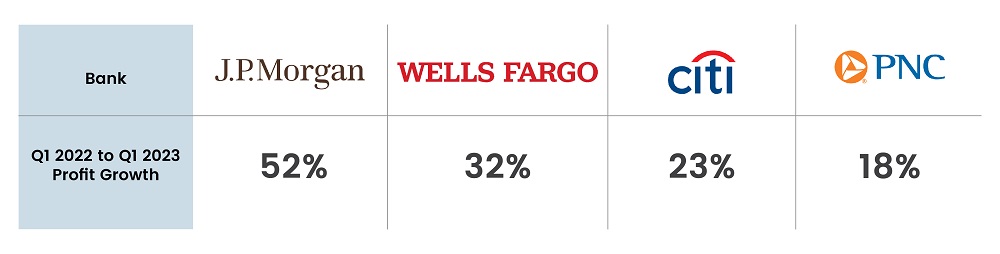
Source: News Nation
Read more: Innovation in Defense Tech: Private Funding Opportunities on the Rise
Big tech companies entry into the fintech and banking industry has the potential to disrupt the traditional banking landscape. While big banks may have the resources and established market presence to compete with these tech giants, smaller and regional banks could be at a greater risk. Big tech companies have significant advantages, such as their scale and resources, established customer bases, regulatory compliance expertise, and strong brand recognition. These factors could give them an edge in developing and deploying advanced banking technologies, marketing and selling their financial products and services, and attracting customers. As a result, smaller and regional banks may struggle to keep up with these new competitors, which could lead to consolidation and a reshaping of the banking industry as we know it.

The impact of big tech's entry into the banking and fintech space is significant and multifaceted. To begin with, it could lead to a shift in customer expectations. As big tech companies set the standard for seamless and intuitive digital experiences, customers may come to expect the same level of service from traditional financial institutions. This could put pressure on banks to invest more heavily in digital technologies to remain competitive. Furthermore, moves like this could lead to new opportunities for collaboration between traditional financial institutions and big tech companies. For example, banks may partner with big tech companies to offer innovative financial products and services or to leverage big tech's expertise in areas such as data analytics.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
Partner of choice for lower middle market-focused Investment Banks and Private Equity firms, SG Analytics provides offshore analysts to support across the deal life cycle. Our complimentary access to a full back-office research ecosystem (database access, graphics team, sector & domain experts, and technology-driven automation of tactical processes) positions our clients to win more deal mandates and execute these deals in the most efficient manner.